Inflammation is not something bad. It is part of the body’s intelligent repair process. This process helps our bodies to heal some damage or irritation or stop infection from occurring. When infection or irritation stops, inflammation calms down and goes away. Sometimes inflammation does not go away. It goes on and on and gets worse. Something is stopping the process from finishing up. In this post, we look at how to stop inflammation when it isn’t stopping by itself.
How inflammation works
When we get an injury (like bumping ourselves on a table corner or a sunburn), our immune system triggers a protective response. When a body part is irritated (burning our tongue on a very hot drink or eating something we are sensitive to) a similar response occurs.
This inflammatory response makes capillaries expand so that healing nutrients can be rushed to the damaged area. Protein-rich blood fluid is forced from the capillaries, acts like a balloon, swelling up to hold the affected area firmly so it can heal. This swelling produces similar conditions to a plaster cast on a broken bone but on a smaller scale.
The inflammatory swelling presses on nerves which can cause pain. This immobilises us because it hurts to move. Our own body is forcing us to stay still – so it can fix the damage. It would be impossible to heal a broken bone if we were jumping around, moving it constantly; in the same way, the inflammatory response works to keep the damaged part still.
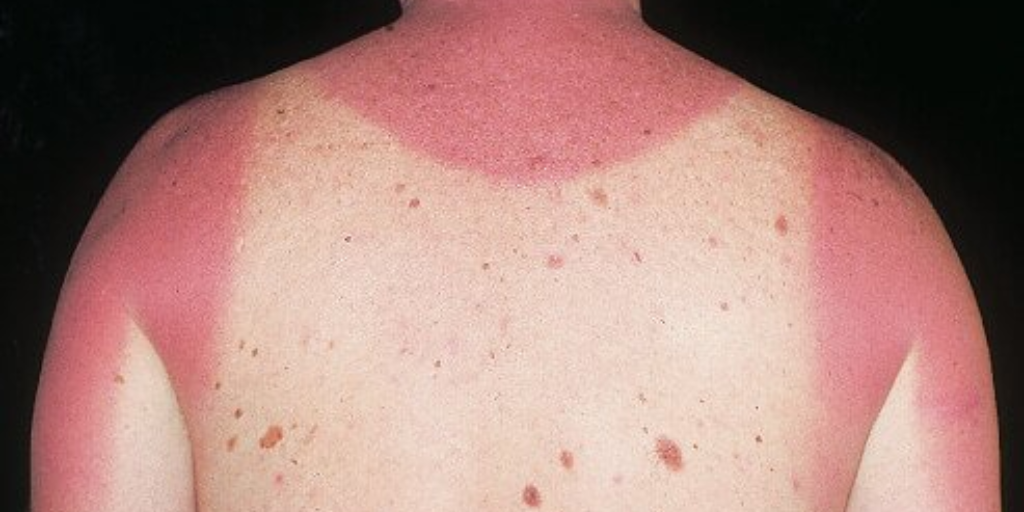
These are some of the signs of inflammation – all parts of the healing process:
- swelling
- pain
- heat
- redness
- loss of function
Pause for a moment and think what an anti-inflammatory pain killer does. It is reducing the above symptoms of inflammation. Is this how to stop inflammation long term? No! This reduces pain and heat, allowing you to move the part the body needed to be kept still! How do you expect healing to come then?
This is how taking drugs works against the body and ends up causing more problems down the track. Take them temporarily, or in an emergency – then work on getting well so you can get rid of them.
Some inflammatory diseases
Sometimes the inflammatory response does not end. Something has gone wrong with the process. When this happens, we call it an inflammatory disease. Sometimes pain is involved and sometimes swelling or heat that cannot be felt is involved.
Inflammatory diseases are intelligent responses of the body to something causing damage.
All the main chronic diseases begin with inflammation. These are not ‘rogue’ diseases; rather, they are the body crying out to be given what it needs to operate a perfectly healthy process correctly.
When inflammation goes on and on for months and years, it injures the body. Damage becomes ongoing and the inflammation response never ceases. It is vital to understand how to stop inflammation before it reaches this ongoing level.
Some of the diseases caused by this type of inflammation are:
- Heart disease: Inflammation injures the lining of arteries. As the body tries to heal them, blood flow is reduced, starving downstream organs like the brain and the heart, leading to chest pain, heart attack or stroke.
- Alzheimer’s: Inflammation causes amyloid plaques and tau nerve tangles to build up in the brain. These damage nerves, leading to Alzheimer’s.
- Mental disease, including depression: All mental diseases have inflammation as their cause – not serotonin deficiency as was once thought. Serotonin production is reduced by gut inflammation.
- Type 2 diabetes: An inflamed pancreas leads to insulin resistance and obesity. Talking about too much sugar is getting the cart before the horse.
- Cancer: Any chronically inflamed part of the body becomes a microenvironment suited for new tumour growth – the main tumour sends out ‘scouts’ to find these areas for new growth.
- Autoimmune diseases are closely related to gut inflammation.
- Arthritis is clearly inflammatory – but is also related to inflammation in other parts of the body.
Measuring inflammation
One blood marker of inflammation is C-reactive protein (CRP). We want this marker to stay between 0 – 5 mg/L. – the lower the better.
With some diseases, like cancer, we may not feel the inflammatory heat. A thermography scan which measures heat radiating from our body, can indicate the inflamed site. Thermography can indicate the presence of cancerous tumours before the typically used X-rays can. It cannot determine if they are malignant, but it can identify their presence clearly.
Anti-inflammatory drugs
Many medications are designed to stop the inflammatory response.
This is how non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) medications such as Nurofen, Voltaren, Naprosen, Celebrex and Disprin work:
- Inflammatory pain occurs when substances called ‘prostaglandins’ build up.
- These prostaglandins are produced by particular enzymes, namely COX enzymes.
- These enzymes produce prostaglandins which promote inflammation, pain, and fever.
- By blocking these enzymes, we reduce pain and fever.
A high blood CRP level shows this COX enzyme system is working overtime. Anti-inflammatories inhibit it from working, thus lowering CRP in a blood test. This looks good – on paper! But block the COX 1 system too often and you increase your risk of ulcers, kidney problems and heart disease.
COX-1 enzymes (one of the two enzyme types making prostaglandins) also produce a prostaglandin that activates blood platelets and protects the stomach and intestinal lining. This means than when taking these drugs, we place the intestinal lining of our stomachs at risk!
<Research shows> non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are responsible for 30% of hospital admissions for adverse drug reactions, mainly due to bleeding, heart attack, stroke and renal damage. This makes it abundantly clear that Westerners are taking too many of them. In other words, too many of us are blocking this enzyme pathway that affects our body’s self-healing inflammatory response. We set then set ourselves up for these more serious diseases down the road.
Continually stopping the inflammatory response causes the body to move to Plan B of its intelligent responses to try to heal the damaged area. This causes more pain, stiffness, tumour growth and auto-immune flares. We can read these responses as the body’s attempts to wall off or immobilise or kill off the damaged parts. Western medicine, however, responds with yet more targeted drugs against these symptoms – while the real problem is something else.
How to stop inflammation naturally
Knowing how to stop inflammation requires looking back to the first inflammatory event and how it was approached. You can read <here> about how treating the cause is a major underpinning principle of nutritional medicine.
We have already looked at how certain pharmaceutical drugs work to stop inflammation. And at the risks of heavy use of these drugs.
Fortunately there are some natural alternatives:
Almost 300 natural substances exert a mild anti-inflammatory effect by blocking the COX enzyme pathway. Some of these are ginger, curcumin (in turmeric) and frankincense (Boswellia serrata). And none of these cause internal bleeding. A big plus! They also do not appear to cause ulcers, heart disease or kidney problems either.
Studies have shown what the therapeutic dose is for each of these in order to get a significant reduction in pain and swelling. (If you are an anticoagulant medication or suffer from liver or kidney disease, check with a nutritionist first.)

With curcumin tablets, usually a minimum of 500mg curcumin, 3x/day is needed. The results should be noticeable.
With ginger, the therapeutic dose is ⅓ tsp/day to 1 full tsp/day powdered ginger being as effective as ibuprofen for stopping period pain. You can read more about using ginger therapeutically for pain <here>.
What’s the drawback?
They still block the inflammation process itself – which is part of the body’s self-healing mechanism. They may stop the headache or period pain or arthritic pain (randomised trials say they do this AS WELL AS common drugs sold for this purpose) – but they still don’t fix the problem.
Lifestyle medicine lowers inflammation
Changing our lifestyle can dramatically lower inflammation – indicated by CRP levels on pathology tests:
- Exercise: Walking for only twenty minutes significantly reduces inflammation markers in the blood.
- Stress also increases chronic inflammation. Reducing stress has an overwhelming effect on our health at all levels.
- Social isolation also increases inflammation. The effort we put into starting and maintaining relationships within a community will pay off hugely in our health in the long run. Read more <here> about how loneliness affects our health.
How to stop inflammation with food
Certain plants contain substances that control how chemical messengers outside the cells can speak to the genes inside, regulating how those genes act. These substances protect the plant from pests, mould and the sun’s radiation. They are called “phytonutrients” and are what give plants their colours, smells and tastes.
These phytonutrients in plants actually affect our own cell function when we eat them. They bind to cell receptors on cell walls and translate their message into the cell where the genes read and respond to the message. It’s almost like eating a microchip and having the computer message start regulating our body! In this way, certain plant foods can step in and get our inflammatory response under control.
This is one reason why adopting a plant-based diet improves inflammatory diseases.
Phytonutrients are not drugs. They are not concentrated, but have a mild effect, speaking to our genes gently and quietly. This ensures that we do not experience violent hormonal swings when we consume them. Their effects are subtle and intricate as they control how our genes respond to environmental changes.
The key is to eat them in large quantities. Over time, these phytonutrients will keep our cell systems running smoothly, including keeping inflammation under control.

In one study, heart disease patients were placed on either a whole-foods vegan diet or an American Heart Association diet. In only eight weeks, CRP was significantly lower in the vegan group (despite the same weight loss in both groups). Their arteries were healing better, reducing heart attack risk.
There are different categories of phytonutrients with different jobs. To make it easy, just eat many colourful plants. This is how to stop inflammation: eat a whole lot of plant foods.
Organic foods and inflammation
Organic foods generally contain more of these ‘chemcial messenger’ phytonutrients. Here is why:
- No pesticides or herbicides are used when growing plants organically.
- This means the plant must protect itself to survive.
- Bug and parasite attacks stress the plant.
- Plants under stress manufacture more bitter phytonutrients in self-defence.
- When we eat these phytonutrient-rich organic plants, these anti-stress (anti-inflammation) agents go to work in us.
The more bitter the flavour, generally, the more phytonutrients are on board. This is a major reason to learn to love ‘bitter’ and reach for organic vegetables and fruit wherever possible.
Inflammation and processed foods
Food processing of plant foods removes or damages the phytonutrients we have been reading about. When we fill up on foods containing white flour, sugar, sweets, vegetable oils, deep-fried foods and most baked goods, we fail to eat enough phytonutrient-rich foods to keep us healthy.
Consuming less than 60mL of soft drink per day (1/4 cup – one small mouthful) causes a spike in CRP 30 minutes later, and these markers remain elevated for several hours.
Eating one slice of white bread results in higher blood sugar levels and another inflammatory marker, NFkB.

Remember that phytonutrients must be consumed in QUANTITY to fix something.
This is a major reason to reduce animal foods too – they contain no phytonutrients at all. When we fill up on meat and dairy and eggs, we cannot be filling up on plant foods. This means fewer healing phytonutrients. So don’t fill up on animal foods if you want to bring inflammation under control.
Summing Up
The key from this post is that inflammation is a good and intelligent response from the body – if it works properly.
For the inflammatory response to work correctly it requires certain inputs:
- The right inputs in our lifestyle and diets cause the system to work perfectly – to cause inflammation, then to use the heat, swelling or walling off to get the repair job done. And then, to finish up by halting the process.
- Insufficient and incorrect inputs allow this inflammatory response to occur, but there will be too few ingredients to continue the process to then HEAL the inflamed area.
Medications designed to block the enzyme pathway which leads to inflammation, while they may be necessary to provide some symptomatic relief, are not helpful for growing a healthy body long term.
Natural anti-inflammatories, such as turmeric or ginger, can also block inflammation and reduce the pain, but without damaging side effects. They do not heal, but can be a great option to use while you work on getting well.
Adopting a diet rich in phytonutrients (colourful plants) can potentially fix your body, and get the inflammatory response working as it is supposed to.



0 Comments